Glossary
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZA
Action
An action is one step in the execution of a callflow. An action takes parameters and has exits. For example, the action CallDevices will call a list of devices. The parameters for this action include a time-out and the list of devices. Possible exits are: busy and time-out. If the call is picked up, the action ends without going to an exit. You can find an overview of all the actions in the action reference guide.Active-Active set-up
An active-active set-up consists of two or more SOPs that work together to provide telephony or a unified communication service. The administrator configures an active-active configuration separately for each service: telephony can be put in an active-active configuration separately from the net.Console service, etc. There are two types of active-active set-ups:- Unbalanced active-active set-up: A number of the SOPs act as the primary SOPs while others act as the back-up SOPs. In case of problems with one or more of the primary SOPs, the system will automatically switch over to one or more of the back-up SOPs.
- Balanced active-active set-up: The load is distributed evenly between all the SOPs. In case one of the SOPs experiences problems, all the other SOPs take over the load.
Active-standby set-up
An active-standby set-up consists of a primary SOP and a clone SOP that can take over in case the primary SOP experiences problems.Apply changes
When you make changes in the SMP, these changes affect only the configuration database that is stored in the SMP system. To activate these changes on your SOP or SOPs, you need to use the "apply changes" function. This pushes the new configuration from the SMP to the SOPs in your set-up and you will be able to test your new functionality.APN
Acronym for Apple push notifications: it is used in order to push messages to Apple iOS devices.ATA
An An analog telephony adapter, or analog telephone adapter, is a device used to connect one or more standard analog telephones to a digital telephone system (such as Voice over IP) or a non-standard telephone system. More information can be found atAttribute Log
See SDR / STR.Audio prompt
An audio prompt is an audio message that can be played in certain situations. Uses may be: a welcome message for your company reception, a vocal explanation of a menu ("For ..., press 1"), the name of a user that is read by the voice mail, and so on.Architecture
There are three types of architectures: Active-active setup, Active-standby setup and Standalone setup. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZB
BLF
Busy Lamp Field, light on an IP phone (e.g. Polycom phones) that tells you whether the extension attached to a Speeddial button is idle or busy/ringing. BLF is also the name of the feature, which is also called Supervision or Presence.BRI
Basic Rate Interface: an ISDN line that has a capacity of two simultaneous conversations.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Basic_Rate_Interface
C
CAC
Call Admission control. CAC mechanisms complement and are distinct from the capabilities of Quality of Service tools to protect voice traffic from the negative effects of other voice traffic and to keep excess voice traffic off the network. Since it avoids voice traffic congestion, it is a preventive Congestion Control Procedure. It ensures that there is enough bandwidth for authorized flows.CAG
Camel Anchoring Gateway: CAG or Camel Anchoring Gateway provides the SS7 connectivity. Its the application which replies to the routing requests received by the MSC. Its received the Camel signalling triggering. It also takes care of the interface with the HLR. Summary, CAG is a border server with the provider core network and has the goal to manages mobile signallingCallflow
When a call comes in, certain actions can be taken before it is sent to a user. For example, the caller can hear a voice menu (IVR) and make a choice. Depending on this choice, the call could be sent to a user, to the reception, to a voice mailbox, to another IVR, and so on. A callflow is a scenario that uses one or more actions to implement what will happen to the call.CDG
Call Distribution Gateway: CDG or Call Distribution Gateway is a border servers with the provider. Its goal is to manage the voice and signalling for all calls. This gateway takes care to have all information to route the calls to the right FMU and to ring the FMU mobile phone.Communication Flow Studio
A visual environment to help you define your callflows.Communication Routing
The solution has a list of internal numbers (extensions) and external numbers (the DDIs you get from your operator). Communication Routing routes incoming calls from an external number to an internal one and outgoing calls from an internal number to one of the ways to make external calls (e.g. ISDN, a SIM box, VoIP, ...). Also, calls can be routed internally using callflows.CFB
Call Forwarding Busy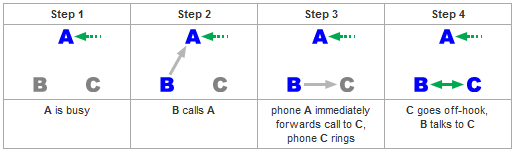
CFU
Call Forwarding Unconditional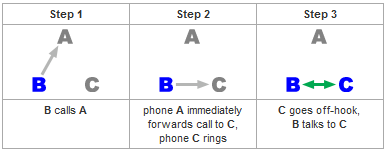
CFNR
Call Forwarding No Reply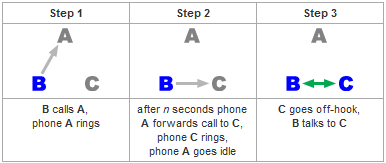
CDR
Call Detail Record: a record of a (billing) event produced by a SOP- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Call_detail_record
Clone
A clone is an identical copy of a SOP used in an Active/Standby architecture that can take over (manual operation) in case the corresponding haMaster SOP goes down.Cluster
A cluster is a bunch of SOPs that are configured to work together on the processing of the telephony and/or unified communication applications of one large organisation. A cluster of SOPs is defined as a number of SOPs linked to the same master SOP. Those SOPs have the same configuration except modules and SOP Key configuration. A cluster of SOPs is possible for all types of architectures (active-active, active-standby and standalone).Codec
A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding and/or decoding a digital data stream or signal. SeeCOLP
Connected Line Identification Presentation. The service available with Communication Server 2 allows to see the name and the number of the connected party which is ringing or the one we are in conversation with.Consolidated management
The transparent management of more than one SOP as if it was only one. With the unified communication solution, you can manage the users, the directory, callflows and resources of all SOPs at once. This is similar to having a set-up with several traditional PABX systems with unified communication, yet you can manage the whole set-up from one web interface.CSV
Comma Separated Values: a format that is used to import and export databases.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Comma-separated_values
CUG
Closed User Groups: Are groups of subscribers who can only make calls and receive calls from members within the group.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Closed_User_Group
D
DDI/DID
Direct Dial-In/Direct Inward Dialing: usually refers to a range of telephone numbers that your contacts can use to call users in your company. These are external phone numbers and can be mapped to internal numbers or to callflows.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Direct_Dial-In
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: a protocol used to map internet addresses (e.g. www.google.com) to their IP addresses.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:DHCP
Directory
The directory is an extensive version of what used to be a phone book. Because this is a unified communication solution, the directory contains not only names and phone numbers, but also the e-mail address, a fax number, the department, a default callflow, and so on. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZE
EndPointAbstraction
Concept used to abstract a cell phone into a regular SIP phone. This is done on the (v)NAG using EndPointAbstractionInterface resources on the SMP. Those will register on the customer PBS like any SIP phone.ETC
Extension Terminated Call: call destined to the users short number on the company PBX.ETL
Escaux Templating Language, can be used to write expressions inside the Service Creation Environment in order to build powerful and directory centric services.Event
The SOPs keep an event log for tracing problems. The principle of this event log is similar to the syslog.Extension
An extension is an internal phone number. For example, 100 can be assigned to the central reception desk. A user can have more than one extension: one for his desk phone, one for the softphone on his PC, one for his mobile phone, and so on. Extensions can also exist without a link to a user: the extension to listen to your voice mail, an extension where a caller first gets a menu (IVR) before the system transfers him to another extension, and so on. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZF
Firewall
A firewall is a (part of a) computer system that acts as a protection between a secure network, like the network in your organisation, and an unprotected network, like the Internet.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Firewall
FMU
Fixed Mobile Unification is the unique Escaux service allowing to convert (emulate) any cell phone into a corresponding cloud located SIP end-point. This is implemented in a Network Abstraction Gateway (NAG).FMU endpoint
The FMU endpoint is the virtual endpoint that which registers in the customer's PBX (line registration) and which is mapped to a mobile phone.FTC
FTC stands for Fixed number Terminated Call: call destined to the users landline number, on the company PBX. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZG
Global parameter
In callflows, the administrator can use global parameters to make the execution conditional. He can set the value of the global parameters using the SMP.GCM
Acronym for Google Cloud Messaging: used in order to push message to Android phones. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZH
haMaster
Name given to the main SOP in an Active/Standby architecture. The second SOP is the "Clone SOP". Either the haMaster or the Clone SOP can have the role of Active or Standby.High Availability
Implementation name for the Active/Standby architecture. Active/Active setup's rely on Cluster architectures and does not make use of the High Availability module. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZI
In-Band Signaling
a way to send metadata and control information within the same band (channel) used for voice; e.g. DTMF tones. Therefore it can be heard by the callers! (see also: Out-of-Band Signaling)ISAP
The acronym for Internet Service Access Point. This server is a reverse proxy. All requests coming from the internet (Escaux Connect clients) will pass through the ISAP and will be directed to the correct SOP.IVR
Interactive Voice Response: a menu system for telephony that reads the menu items and that allows users to make their choice using the numeric keys of their telephone.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Interactive_voice_response
J
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZK
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZL
LDAP/Active Directory
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. Microsoft Active Directory is one example of a database that uses the LDAP protocol for querying and modifying data in a directory.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:LDAP
LS
LS or Location Server allows the communication between border servers. It plays several roles:- Provide information about the call in progress: IMRN (temporary numbers to route the call), Camel information, etc.
- Provide static information about number: all customer numbers are stored in its database.
- Provide topology information: there is a mapping between all number and the FMU where the user is registered.
LUA
SMP 4.10 introduced a scripting language based onM
m.Connect
The former name of the application Escaux ConnectMAC
Move, add, change: an operation that adds, moves or modifies certain parts of the configuration. Usually, a MAC operates on basic components like users or phones. This is in contrast with set-up operations like installing a new set-up at a site, or operations that have an impact outside of the component itself. For example, modifying the set-up of a reception may have an impact on the number mapping, software installation for the receptionists, the internal queuing structure of the reception, and so onMaster resource
A resource defined as Master Resource can contain configuration that can be inherited by other resources during provisioning. That way a standard configuration can be applied to all resources without requiring to duplicate and update configuration in other resources. Not to be confused with Template resources.MOC
Mobile Originated Call: call placed by a mobile phone.Module
The unified communication solution is a modular system. Each module implements one set of features. You can find an overview of all the modules in the module reference guide.Media link
A media link is a virtual connection between different devices (SOP's, phones, net.Desktop clients, ...) inside a Unified Communication network. These connections can be of any type and any technology and typically correspond to a set of media parameters to be used between two different sites.MSS
MSS stands for Mobile Switching center server. MSC or Mobile Switching Center is responsible for routing voice calls in the provider GSM/CDMA network. It sets up, releases and manage the end-to-end connection during the call. Mobile Switching Station or MSS is an MSC Server.MTC
Mobile Terminated Call: call destined to the main mobile phone number.Music-on-hold
When a caller is put on hold, the system will play music-on-hold as an indicator to the caller that his connection is still active. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZN
NAG
Network abstraction gateway. The NAG is a gateway being located in the mobile operator's network. It exposes the mobile devices as SIP end-points towards the customer's call control platform.NAT
Network address translation, also known as masquerading, is a widespread technology to convert a private IP into a public IP and vice versa.net.Desktop
The software client for unified communication. Depending on the version, net.Desktop offers a unified directory, status and presence management, voice mails, fax, video, chat, SMS and more.net.Console
The software client for receptionists. net.Console offers an intuitive graphical user interface that enables operators and receptionists to quickly answer and process calls.net.Supervisor
The software client for call center supervisors. net.Supervisor offers a configurable graphical dashboard that shows statistics about the processed and unprocessed calls, the agents, the callers, the queues and other call center components. net.Supervisor can also be used on a large screen as a status billboard for the call center. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZO
OLO
Other Licensed Operator.Out-of-Band Signaling
a way to send metadata and control information using a different band (channel) that the one used for voice. Therefore, it cannot be heard by the callers! (see also: In-Band Signaling) A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZP
PRI
Primary Rate Interface: an ISDN interface that has a capacity of thirty simultaneous conversations.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Primary_rate_interface
Presence
See BLF.Probe
For proactive monitoring, the SMP uses probes that check the state of certain hardware and software subsystems on the SOPs. The administrator can configure these probes from within the SMP web interface.Profile
Each user is assigned a profile that determines what role he plays in the organisation. For example, a director has different needs for communication than a sales person or an administrative employee. The profile determines which statuses the user can choose between.PUM
Personal User Mobility (PUM) allows a user to move from one desk to another while having his personal settings on any phone of the same brand. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZQ
QDR
Queue Data Record: Used for reporting on queues. QDR reports can be summarized by queue, agent, call result, time, date, caller or called numbers.Queue
A waiting row for calls or for other unified communication. When used for calls, a queue will act as a waiting buffer when the calls come in faster than they are answered. Calls will leave the queue in the order they came in. For that reason, queues are also called FIFOs (first-in-first-out).- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Automatic_call_distributor
R
Resource
Resource is a generic name for several components that you use while setting up your solution. These include the phones, call queues, probes to monitor your solution, and much more. You can find an overview of all the resources in the resource reference guide.Restriction group
A list of restrictions, for example: can make calls to national numbers but not to international numbers. A phone will be put in a restriction group to restrict the calls that can be made from it.RMA
RMA stands for or Return merchandise authorization. The delivery address for RMA is ESCAUX sa - Chaussée de Bruxelles, 408 - 1300 Wavre - Belgium. The RMA number is the incident ticket number received by using the incident management process.Route
In this context, a route is a pattern in a telephone number that is linked with an action that needs to be taken for these numbers. For example: for all numbers starting with 004, send the call to a SIM box.Route group
A collection of routes. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZS
SBC
a Session Border Controller is a device regularly deployed in VoIP networks to exert control over the signaling and usually also the media streams involved in setting up, conducting, and tearing down telephone calls or other interactive media communications. Typical tasks of an SBC include: topology hiding, protection against malicious attacks, quality of service, media services, reporting,...SCE
SCE stands for Service Creation Environment. The SCE is part of the SMP and allows to define and configure a Service Template based on a set of Escaux building blocks. The Forced on PBX and Fixed-Mobile Unification services are examples of Service Templates. The SCE can be used to define relevant customized services in a functional way. The configuration can then be pushed on a set of SOPs or vSOPs.SDR/STR
State Duration Record / State Transition Record: used for reporting on the presence. The system will log an STR every time a user changes his intentional status, logs in or out of a queue, every time a PUM status changes,... An SDR is then the amount of time that the user spent in one state before it was changed. An SDR, just like a CDR has a start time and a duration. An STR only has a timestamp. STR's are also known as Attribute Log.Service Portal
Application used by the partner to open ticket, to have an overview of them and to communicate with the incident management team. (http://escaux.com/service). This application is protected by a login and a password.Site
Physical location where one or several SOP's and phones are deployed. Several network subnets can be attached.SMP
Service Management Platform, used to configure any Escaux solution. Also the name given to the Cluster of machines that runs the SMP Application (web gui), SSH Routers and BMS.SMP-Admin
Escaux administration interface for an SMP, dependency of the SMP Application (web gui) and also common layer for multiple SMP Application instances. Not to be confused with the smpadmin access level on the SMP Application (web gui)Snapshot
A snapshot contains a back-up of your complete configuration at a certain point in time. You can make a snapshot before you change an important item. In case your change results in problems, you can restore the snapshot to undo the change.Software Lifecycle
- ED - Early Deployment : the version is ready to be used by any customer, but should be used with care. Minor problems are to be expected.
- GD - General Deployment : the version is ready to be used by any customer.
- EOL - End of Life : the version will not receive any support.
SOP
Service Operational Point: an appliance that executes services. You define the services you want in the SMP by defining users, the resources they use, the callflows, and so on. The SMP only offers a website for configuration. For the execution of these services, you will have one or more SOPs that can be installed on-site, in a datacenter, or anywhere that is most practical for you. When your users make a call with one of their telephones, or they use unified communication with one of the software clients, the phones and software will contact the SOP to start the requested service.SOP key
A unique identifier of your SOP. A SOPkey is a number with 8 digits (e.g. 00000004).SOP Shell
While all configuration is done using the SMP, each SOP also offers a local shell for checking the status of the SOP and its subsystems and for local debugging. The SOPShell should only be used for troubleshooting purposes.SSH
Secure Shell: a secure network protocol that is used for communication between the SMP and the SOPs.- More information can be found at
Wikipedia:Secure_Shell
Standalone setup
There are 3 types of architectures, one of them being the standalone setup with only one SOP. The other architectures are the Active-active setup and the Active-standby setup.Status
A user can tell the system what situation he is in, for example: in meeting, at his desk, working from home, on holiday, and so on. The unified communication solution will use the status to decide what to do with incoming calls. The reason behind this system of statuses is that it makes no sense if a telephone rings when its user is on holiday.Supervision
See BLF.System task*:
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZT
Template
A set of pre-defined features that are documented, validated and supported.Template resource
A resource included in a Template (source is Template) A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZU
UCS
The acronym for Unified Communication Solutions.UEP
The acronym for Unified End Point. The Unified End Point vSOP serves as backend server for the Escaux Connect end user web app. It works in combination with a WebRTC vSOP in the same cluster of vSOPs in order to provide UC services.Unification Point
A Unification Point (UP) represents the right to use a part of the software on a Service Operational Platform (SOP). UPs are sold to operators or service providers in bulk only. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZV
Versioning:
Escaux uses a 3-digit (preferred} and 2-digit sequence based identifier, separated by a '.' : major.minor.bugfix . Each sequence can consist of 1 or multiple digits. A first GD release has a major number higher than 0.- major: Contains significant new features
- minor: Contains new features or improvements and optionally bugfixes.
- bugfix : Contains only bugfixes.
Virtual profile
When a set-up uses personal user mobility (PUM), the users can log in and out on a phone. In case a user is logged in on a phone, this phone is configured with his profile. In the case no user is logged in, the phone is configured with a virtual profile.VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network. For some purposes, it makes sense to install a second LAN in order to separate one kind of traffic from another. A typical example is IP telephony: telephony is a real-time application and requires predictable bandwidth. On the other hand, a normal LAN can be used by all the computers for any kind of communication they need to do. If several computers are transferring large files, IP telephony can slow down if it works on the same LAN, which decreases the audio quality and can result in dropped audio. VLANs are a way to implement a "virtual" separate LAN network on the same physical hardware: IP telephony will get a guaranteed percentage of the bandwidth to make sure audio quality is good, while the rest can be used by the computers for their purposes. More information can be found atvNAG
Virtual Network Abstraction Gateway. NAG implemented on a vSOP.vSOP
Virtual SOP. vSOP's are contained in physical SOP's (vSOP host). vSOP's are configured like any SOP on the SMP, it has a SOPKEY and behaves like a regular SOP for all mechanisms (SMP connection, modules installation,..). Network interfaces (eth0 and eth1) are emulated and seen as normal network interfaces by the vSOP. A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZW
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZX
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZY
A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H-I-J-K-L-M-N-O-P-Q-R-S-T-U-V-W-X-Y-ZZ
Some work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Copyright © Escaux SA
